Table of Contents
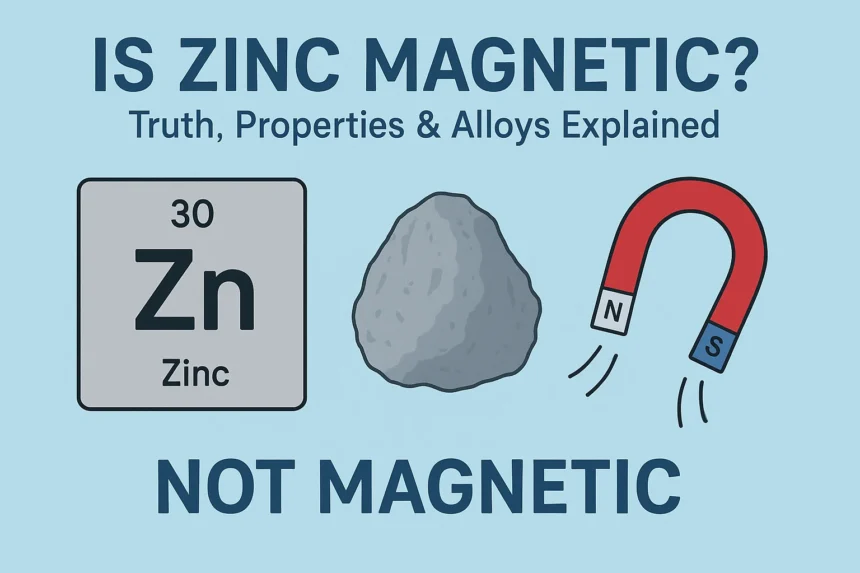
Is Zinc Magnetic?
Many people are surprised, is zinc magnetic? Simple Answer: No, Zinc is not a nonmagnetic metal with a weak diamagnetic property, which means that it really repels magnetic fields rather than being attracted to them. Its atomic structure ([AR] 3D⁰ 4s) has no unpaired electron, which means that it cannot build magnetic bipoles such as iron or nickel.
The study confirms that zinc’s magnetic sensitivity is.31.34 × 10⁻⁵ and its relative permeability is ~ 0.99986, which is almost similar to a vacuum. This means that its magnetic response is very short – weakened about 100,000 times compared to metals.
Even the powerful will not show 1 tesla of magnetic field under magnets, zinc sticks, or visual movement. Scientists can measure their unconscious reaction in laboratory conditions using superconducting magnets compared to only 5 Tesla.
This makes a great option for use in places where magnetic intervention must be minimized, including electronics, accurate equipment, and galvanization processes.
This behavior is also studied under zinc in magnetic field experiments, where researchers analyze its response to strong magnetic forces.

Zinc Magnetic Properties & Research Data
Zinc in magnetic field: understanding its behaviorZinc in magnetic field experiments suggests that zinc is a diamagnetic metal, which means that it slightly repels magnetic forces rather than attracting them. When the zinc is placed in a strong magnetic field, it creates a weak anti-area, causing a small response.
This property is different from metals like iron or nickel. Scientists study the magnetic properties of zinc for electronics, coating technologies, and applications in material science. Understanding zinc in my magnetic field interaction also helps in rust safety research, as zinc is used widely for galvanization and prescription purposes in industrial and chemical environments.
Zinc diamagnetic or paramagnetic: Zinc is precisely diamagnetic, no longer paramagnetic, because its electrons are fully delivered. This makes it one of a kind from materials which include aluminum, which might be paramagnetic and are weakly attracted to magnets.
Zinc magnetic homes: Zinc is diamagnetic, with magnetic sensitivity of –1.34 × 10⁻⁵. This method means that its response to magnetic fields is extremely vulnerable and poor, resulting in minor repulsion.
Zinc magnetic conduct: Zinc suggests no everlasting magnetization and does not maintain any magnetic discipline after exposure. Its conduct is anticipated and regular in all temperatures and situations.
You might also like to read our detailed guide on Why Does My Projector Have a Dark Spot?.
Why Zinc is Non-Magnetic
So when asking “zinc magnetic” in real-world scenarios, the answer is still no, it does not stick to the magnet, and cannot be. When people see that “zinc-carried” objects attract magnets, it is usually under the steel core, not due to zinc.
Factors that make zinc non-magnetic: The main factors that make zinc non-magnetic include its full electron shells, the absence of unpaired electrons, and its diamagnetic properties. These characteristics prevent zinc from aligning with magnetic fields, which repel instead of attracting magnets. It suits zinc coatings and corrosion-resistant applications.
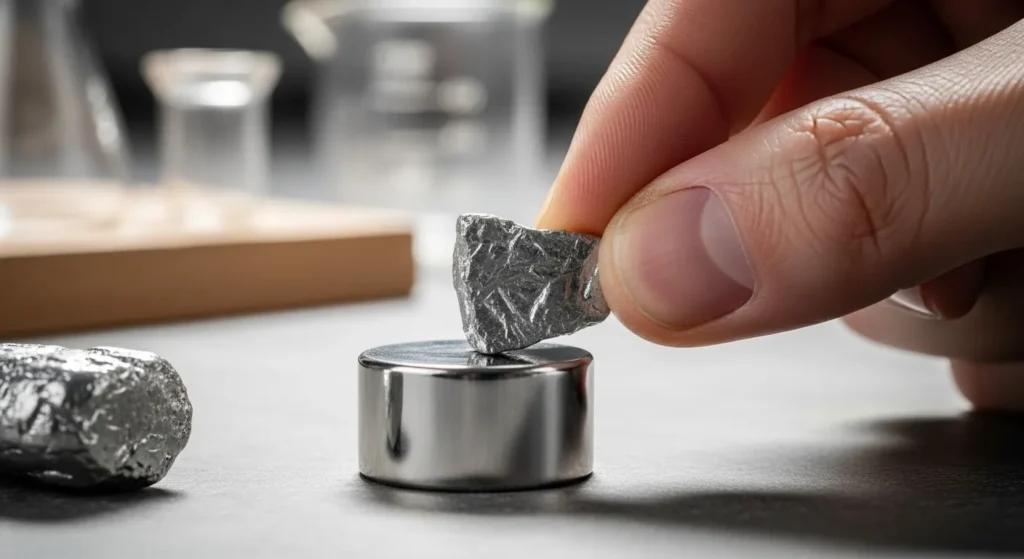

What zinc sticks to a magnet:
Natural zinc does not persist with a magnet under normal conditions. Any sticky conduct is caused by the presence of impurities or an underlying metallic core.
Galvanized Zinc & Zinc Alloys Explained
This is especially true of galvanized zinc, which is a thin layer of zinc (about 7–12 μm) on steel. Magnets are clinging to steel, not zinc.
Jasti zinc is magnetic: Zinc coating on galvanized metal is non-magnetic; however, steel is a magnetic substrate, which is why a magnet will nevertheless cling to the steel.
Zinc alloy magnetic residences: Most zinc mixes, including brass, are nonmagnetic and continue to be. However, while alloys with iron or nickel, weak magnetism may seem because of the presence of ferromagnetic components.
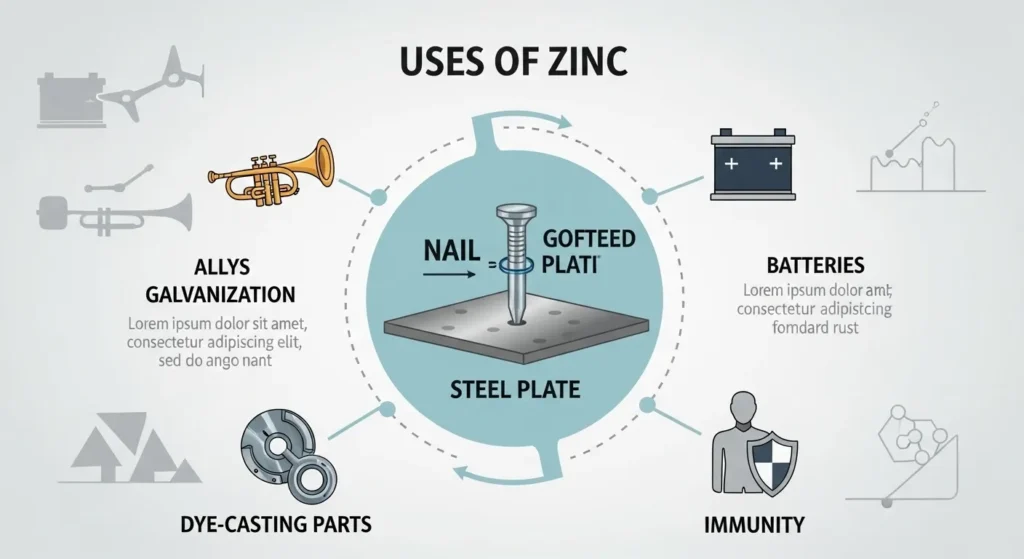
Applications of zinc metal
The most commonplace utility of zinc is galvanization, which protects metal from rust. Zinc is also used in alloys, including brass, dye-canning parts, and batteries. In addition, zinc plays an important role in immunity. Its precise residences make it valuable in the production, motor car, and production industries.
Final Thoughts
Zinc is not magnetic – and it is one of its biggest benefits. Its diamagnetic properties mean that it does not stick to the magnet, does not have residual magnetism, and does not interfere with sensitive devices. Whether you are checking the liberal steel at home or working in manufacturing, the answer to “Is Zinc Magnetic” ensures proper material selection, and when the magnets are used to test metals, confusion is avoided.