Table of Contents
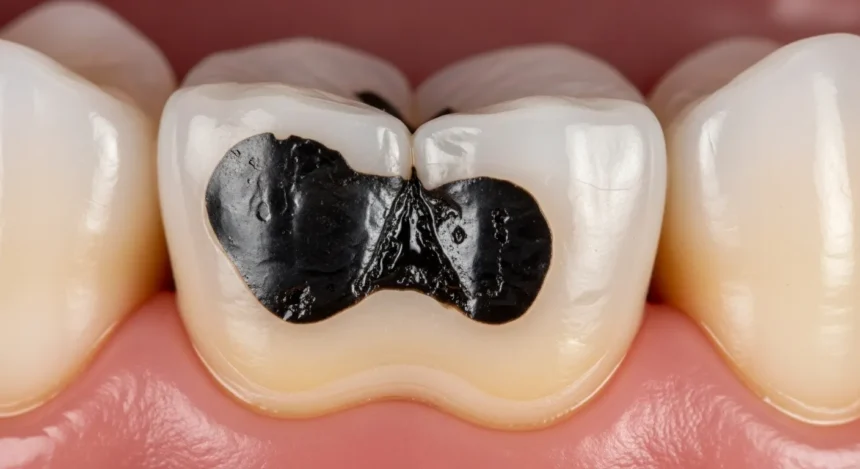
Given that your tooth broke in half black inside no pain, there can be no pain. Color adjustments and breaks may additionally look excessive, but the absence of pain confuses many people.
In truth, pain is not the simplest sign of dental trouble. A black or brown interior typically means that the tooth has suffered inner damage, tooth decay, or even pulp necrosis, the silent demise of the nerve tissue in the pulp chamber.
Understanding that a tooth broke in half black inside no pain, what it means for your oral fitness, and the way to restore it, will help you shield your enamel before the problem spreads.
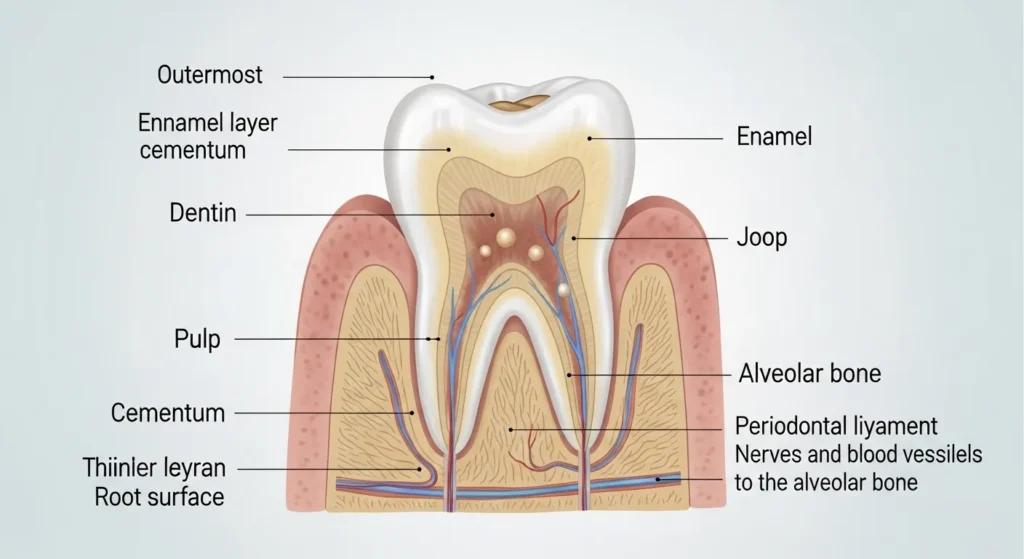
Understanding the Layers of a Tooth
A wholesome tooth is a product of three main layers:
1. Enamel: Shiny, inflexible surfaces commonly crafted from calcium that mildew inner structures.
2. Dentin: The Yellow layer underneath teeth that contains sensations and makes up most of the body of the enamel.
3. Pulp: The soft indoors core filled with veins, blood vessels, and connective tissue.
When trauma, tooth decay, or oral bacteria smash those layers, there can be contamination or pulpitis.
If untreated, the pulp dies, inflicting malaise and, sooner or late,r a black or brown indoors frequently visible when the tooth broke in half black inside no pain occurs.
Why Does a Tooth Broke in Half Black Inside No Pain?
If your tooth broke in half black inside no pain, there are various feasible reasons.
1. Deep Tooth Decay
Untreated dental cavities steadily damage teeth and dentin. As bacteria attain the pulp, tissue disintegrates and blacks the interior of the tooth. The outer shell can, in the long run, fracture due to the fact that decay weakens the internal form.
2. Tooth Trauma
A tough chew, fall, or twist of fate can harm the blood vessels in the pulp. When inner bleeding or nerve dying occurs, the teeth progressively turn black from the inside.
3. Pulp Necrosis
When the pulp dies, it now does feels ache, which explains why breaks might not hurt. The dark color comes from disintegrated nerve tissue trapped inside the pulp chamber.
4. Enamel Erosion
Acidic food, sugary drinks, and negative oral hygiene cause tooth erosion. Without its defensive shell, dentin and pulp grow to be exposed to bacteria, principal to harm, malaise, and cracks, a common cause of teeth spoiling in half of black inner no pain.
5. Metal or Amalgam Filling
Old amalgam fillings (additionally referred to as silver or mercury fillings) can darken the internal shape. When the enamel later cracks, the interior may additionally seem black or gray.
Why There’s No Pain Even When the Tooth Is Black
Many people expect pain when a tooth breaks, yet there may be none because:
- The nerve has already died due to pulp necrosis.
- The crack has not reached living tissue.
- Chronic infection has destroyed pain receptors.
- The body has adapted to a slow, silent tooth infection.
So, even if the tooth broke in half black inside no pain, bacteria, and swelling can still develop around the root.
Visible Signs That Point to Trouble
Even without pain, warning signs and symptoms encompass:
- A black hole or dark malaise within the damaged location.
- Gum swelling around the affected enamel.
- Slight sensitivity when biting or consuming warm/bloodless fluids.
- Bad breath or unsightly taste from bacterial buildup.
- Gradual unfold of discoloration to nearby teeth.
These clues imply it’s time for a dental visit before it becomes an emergency.
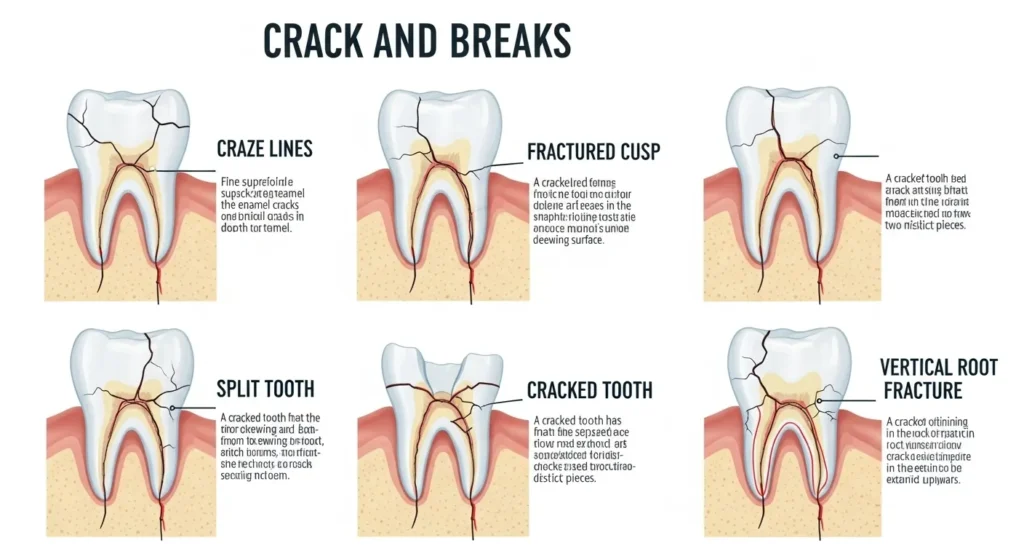
Types of Cracks and Breaks Dentists See
Dentists classify cracks in keeping with severity:
- Craze Lines: Tiny floor cracks constrained to enamel.
- Fractured Cusp: A corner of the tooth breaks, usually close to a filling.
- Cracked Tooth: A vertical crack from crown to root.
- Split Tooth: The tooth absolutely divides typical enamel damaged in half with black inside, no pain instances.
- Vertical Root Fracture: Begins within the root and travels upward, frequently hidden until infection sets in.
What a Dentist Looks for During the Exam
During a dental examination:
- Check the broken floor and surrounding gums.
- Take X-rays to determine if the crack reaches the inspiration.
- Perform pulp power tests.
- Look for pulpitis, nerve damage, or contamination.
If the pulp is vain or the tooth is truly too prone, your dentist will suggest options together with a root canal, crown, or extraction.
Treatment Options for a Tooth Broke in Half black inside no pain
1. Dental filling: For small cracks, filling reduces the segment and seals bacteria.
2. Dental Crown: If half of the tooth is long, but the root remains intact, a crown restores and sees energy.
3. Root canal therapy: When pulp necrosis occurs, a root canal eliminates lifeless tissue, disinfects, and seals the canal exactly.
4. Tooth extraction: If the crack is spread under the gum line, removal prevents infection.
5. Tooth replacement: After extraction, a dental transplant, bridge, or denture restores the characteristic and alignment.
Professional care is important, while a tooth breaks a tooth in half black to avoid internal pain, infection, or further damage.
Why Treat a Painless Black Tooth Early
It may be risky to disregard a tooth with half black inner pain. Although it can look harmless, infections can:
- Spread into the jaw, inflicting a boil.
- Enlighten the gums.
- Weak tooth close by.
- Allow the bacteria inside the bloodstream.
Early dental treatment can often save the teeth with an easy crown or root canal.
Home Care Until You See the Dentist
If you couldn’t visit a dentist properly away:
- Rinse with warm salt water.
- Avoid sugary, hot, or cold ingredients.
- Don’t chunk at the broken facet.
- Apply a cold compress if swollen.
- Brush and floss gently.
These steps help save you from contamination at the same time as looking forward to a remedy. To explore more related topics, make sure to visit our guide on The Dr Pompa Diet & Cellular Healing Diet.
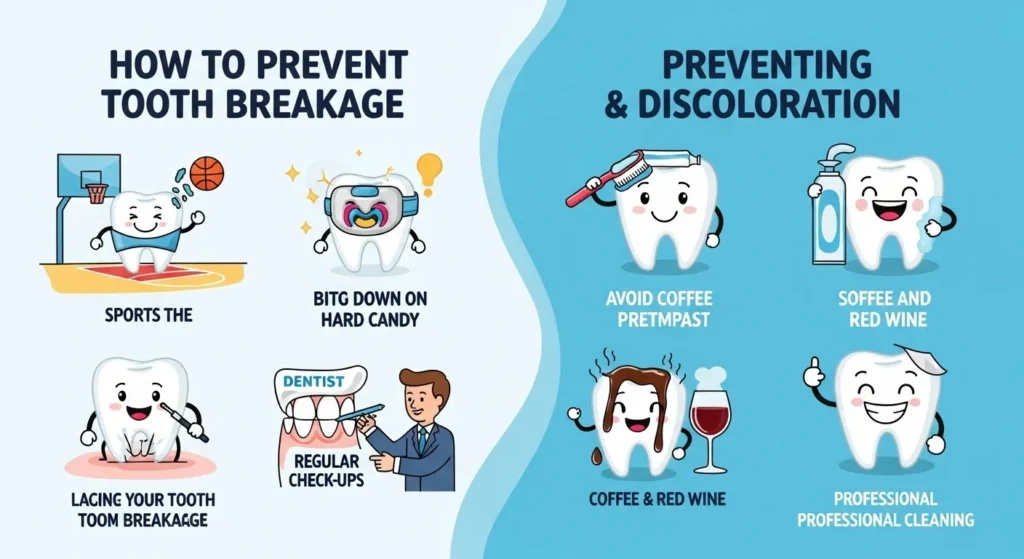
How to Prevent Tooth Breakage and Discoloration
- Brush two times each day with toothpaste.
- Regular floss.
- Limit sugar snacks and acidic liquids.
- Avoid smoking and tobacco.
- Wear a mouthguard at some point in the sport.
- Visit your dentist every six months.
Good hygiene helps prevent conditions wherein the tooth spoils in half of black people; there may be no pain.
Why Teeth Turn Black or Brown Inside
Internal malaise can result in:
- Pulp necrosis
- internal bleeding
- Deep decay
- Some medicinal medicines
- Getting natural
Only a dentist can identify whether the malaise is internal (internal) or exterior (surface-phase).
External Causes of Black Teeth
Not all dark spots indicate decay. Surface staining may occur:
- coffee, tea, or red wine
- Tobacco
- iron supplements
- plaque buildup
- metal filler
These stains are removable with professional cleaning, without any pain in cases unlike the dark interior seen in tooth broke in half black inside no pain.
Managing Sensitivity After Repair
After filling the treatment, the crown, or root canal, mild sensitivity is common.
- Use a soft brush.
- Rinse with mouthwash.
- Avoid excessive temperature.
- Once advised, take mild painkillers.
As the healing continues, sensitivity fades and returns to normal chewing.
Protect your smile for the future
Dental health is a lifetime investment. Regular examination catches cracks before they reach the pulp. Strengthen teeth with calcium-rich foods and avoid acidic habits.
Remember: Teeth do not hurt; no pain keeps your mouth healthy after breaking the teeth in half.
When action is required
If your tooth broke in half, black inside, no pain, it is believed as a serious issue, not a small problem. The absence of pain means it is harmless.
Quick dental care can prevent infection, preserve the natural structure, and restore your smile.
Modern dentistry can rebuild what is broken with care, hygiene, and regular checkups; your teeth can remain strong and bright for years.