Table of Contents
Introduction
Inflammation is your frame’s immune reaction to harm, contamination, or dangerous triggersIt acts like an internal alarm system when danger is detected, your body creates redness, swelling, heat, and pain to protect and repair tissues.
But while short-term inflammation is part of the body’s healing process, long term or chronic inflammation can be harmful.
It often goes unnoticed, leading to serious chronic disease risks such as diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, and even Alzheimer’s.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the early signs of inflammation in the body, how it affects your muscles, joints, and overall health, and the best ways to manage and prevent it naturally.
If you’ve ever experienced fatigue, brain fog, persistent pain, or digestive imbalance, this article will help you uncover whether inflammation is the hidden cause.
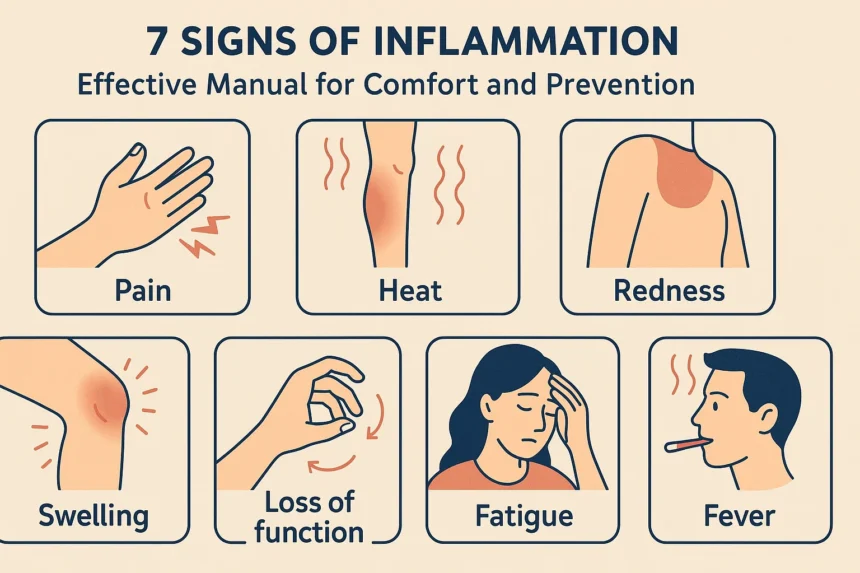
What are signs of Inflammation?
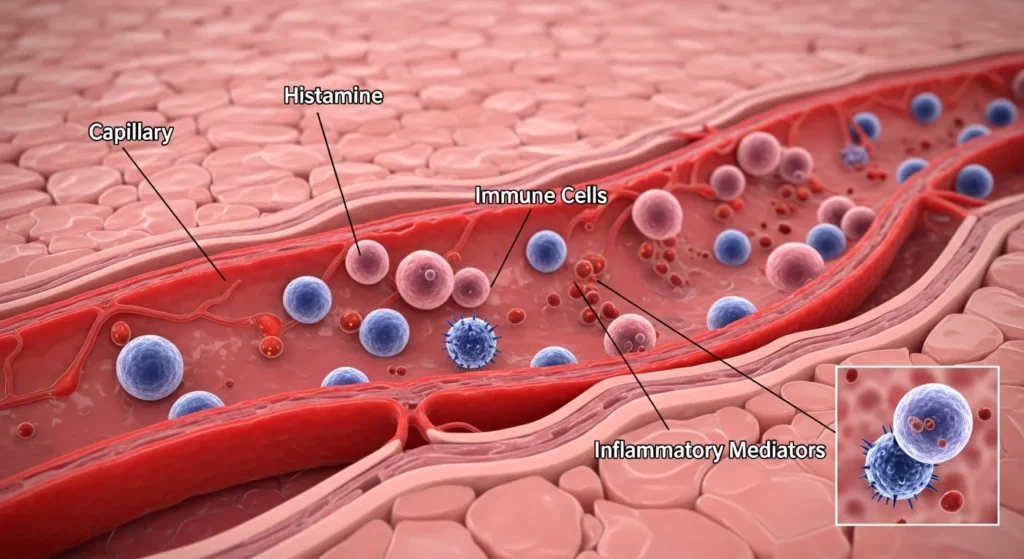
Inflammation is a protective immune reaction that occurs when your body detects harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, or toxins. It also happens when you injure yourself, such as with a cut, sprain, or burn.
- Immune defense: White blood cells rush to the affected area.
- Cytokine release: Special proteins trigger the inflammatory pathway.
- Tissue repair: Damaged cells begin healing.
The Purpose of Inflammation
- Swelling response – boosts blood flow to protect tissue.
- Pain signals – warn you to rest the area.
- Heat response – helps kill bacteria.
- Body’s healing process – begins tissue repair.
While acute inflammation is temporary and helpful, chronic inflammation leads to cellular damage, oxidative stress, immune dysregulation, and long-term health risks.
signs of inflammation in the bodyUnderstanding the signs of inflammation in the body is essential because contamination is your body’s herbal protection against infection, harm, or dangerous substances. However, at the same time as infection will become continual, it is able to negatively affect your basic fitness. Recognizing early signs and symptoms will let you take steps to reduce its impact.
The most unusual signs and symptoms and symptoms of infection inside the body embody redness, swelling, warm temperature, pain, and shortage of characteristic inside the affected place. For example, if you injure your knee, it can grow to be swollen, easy, and warm to touch. These are traditional markers of acute infection. In addition, you could moreover revel in fatigue, fever, and desired soreness whilst infection happens internally.
Chronic infection, instead, might not always be visible however can present as continual fatigue, joint stiffness, digestive problems, or unexplained weight benefit or loss. Conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and coronary heart ailment are regularly related to lengthy term inflammation.
Paying attention to the signs of infection in the frame permits you to make lifestyle changes, collectively by adopting an anti-inflammatory food regimen, exercising frequently, and dealing with pressure. If symptoms and signs persist, consulting a healthcare expert is critical to save you more excessive complications
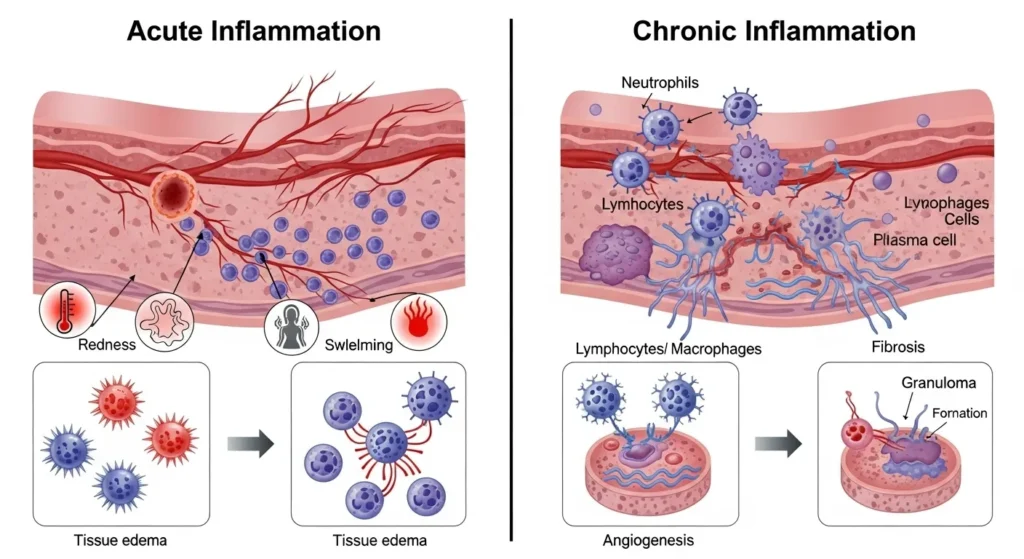
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
- Aspect: Acute-Inflammation/Chronic-Inflamation
- Duration: Short-term (hours to days)
- Long-term (months to years)
- Cause: Injury, infection, cut, burn Autoimmune diseases, poor diet, lifestyle factors
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, pain, heat, loss of function:Fatigue, muscle weakness, joint stiffness, brain fogEffect Protective & healing Harmful & damaging to tissues
Outcome: Resolved after healing/Leads to chronic disease risks
- Acute inflammation = good defense.
- Chronic inflammation = silent enemy.
Symptoms of Acute Inflammation:
Acute inflammation is easy to spot. The classic signs include:
- Redness (flushed skin) – caused by increased blood flow.
- Swelling (fluid retention) – protects the injured tissue.
- Pain signals – due to nerve stimulation and cytokine activity.
- Heat response – makes the area warm to touch.
- Loss of function – stiff joint, limited movement.
Example: If you sprain your ankle, it becomes red, swollen, hot, and painful classic acute inflammation.
Symptoms of Chronic Inflammation:
Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation develops slowly and can be harder to detect. Signs may include:
- Persistent fatigue and body fatigue
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Muscle weakness and mobility issues
- Digestive imbalance (constipation, diarrhea, acid reflux, gut inflammation)
- Brain fog, memory loss, cognitive decline
- Low energy and insomnia
- Skin problems (rash, discoloration, dry eyes
These signs of inflammation in the body may appear mild at first but often lead to serious problems if ignored. Click here to read this article 7 Powerful Ways to Boost Your Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) for Faster Weight Loss.
2025 research advancements for detecting inflammation?
Recent breakthroughs in 2025 are enhancing the potential to hit upon and recognize inflammation, particularly in chronic and systemic conditions.
New approach to the use of antibodies
Researchers at Case [Western Reserve University] developed a method to stumble on specific infection-particular biomarkers in the blood using antibodies.
This method ought to cause new blood tests capable of identifying infection in unique organs, such as those laid low with heart disease or (Alzheimer’s.)
Identification of new inflammatory proteins:
Granzyme K (GZMK): A Harvard Medical School takes a look at recognized Granzyme K as a driving force of infection and tissue damage in autoimmune illnesses. This protein may be a brand new target for treating inflammatory situations.
WSTF protein: A Mass General Brigham took a look at recognizing the WSTF protein as a capability goal for blocking off chronic infection without interfering with acute immune responses.
Link between brain infection and cognitive decline:
Research in 2025 in addition explores the hyperlink among neuroinflammation and dementia, doubtlessly brought about by using elements like positive viruses.
A study in Nature identified certain pro-inflammatory cytokines, like PDGF-AA and RANTES, that are related to faster cognitive decline in older adults.
Conditions Linked to Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is not just discomfort it’s linked to multiple chronic diseases:
Autoimmune diseases rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease.Metabolic issues obesity, kind 2 diabetes, insulin resistanceCardiovascular problems heart disease, vascular damage, arterial plaque, blood clotting.
Neurodegenerative diseases Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, depression, anxiety.Respiratory diseases asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Muscle and joint issues fibromyalgia, myositis, cartilage breakdown. Silent inflammation can remain unnoticed for years, causing damage before symptoms appear.
Muscle Weakness and Inflammation.One overlooked sign of inflammation in the body is muscle weakness.
How Inflammation Affects Muscles
- Inflammatory cascade damages muscle fibers.
- Immune overreaction triggers muscle stiffness and pain.
- Systemic response affects energy levels, causing fatigue.
- Signs of Inflammation-Related Muscle Weakness
- Sudden or gradual weakness in arms, legs, or back.
- Difficulty climbing stairs or lifting objects.
- Muscle stiffness, cramps, or spasms.
- Weak grip strength
When to Worry: If muscle weakness happens suddenly, is severe, or is accompanied by fever, rash, or breathing difficulty, seek immediate medical help.
How to Reduce Inflammation Fast
When inflammation strikes, quick action helps.
- Immediate Relief (RICE Method)
- Rest – protect the area.
- Ice – reduces swelling.
- Compression – controls fluid buildup.
- Elevation – decreases blood flow and swelling.
Other Quick Solutions
- NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin) – reduce pain and swelling.
- Stress management & sleep – lowers hormonal imbalance and circadian disruption.
- Hydration – helps flush toxins.
Prednisone for Inflammation
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication used to control severe inflammation.
- How it works: Suppresses immune response and reduces cytokine activity.
- Uses: Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, asthma flare-ups, severe muscle inflammation.
- Risks & side effects: Weight gain, insomnia, immune suppression, blood sugar spikes, mood swings.
- Warning: Prednisone should only be used under medical supervision. Long-term use carries risks.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
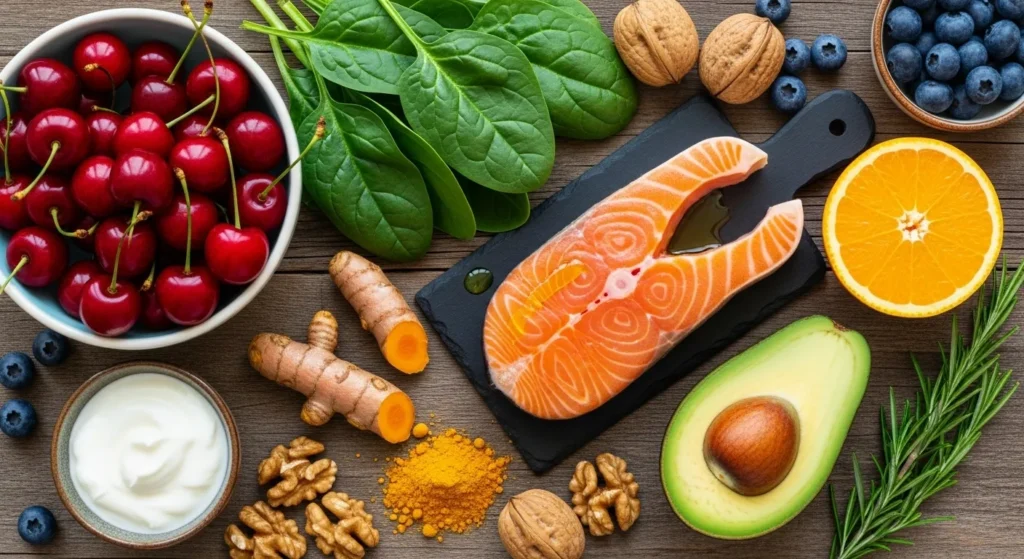

What you eat can calm inflammation naturally.
Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods:
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines, tuna) rich in omega-3.
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, broccoli) packed with antioxidants.
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries) high in flavonoids.
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts) are healthy fats.
- Olive oil cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet.
- Turmeric & ginger powerful natural remedies.
- Garlic supports the immune system.
Foods That Cause Inflammation
Avoiding pro-inflammatory foods is just as important:
- Processed meats (hot dogs, deli meats)
- Refined carbs (white bread, pastries)
- Sugary drinks (soda, energy drinks)
- Fried foods and fast food
- Excess alcohol
- High salt foods and trans fats
- These foods fuel apro-inflammatory state, worsening symptoms.
Preventing Inflammation Naturally
Long-term prevention is key.
- Lifestyle Strategies
- Balanced diet – stick to anti-inflammatory foods.
- Regular exercise – reduces fat and improves circulation.
- Stress control – meditation, yoga, deep breathing.
- Adequate sleep – restores immune function.
- Avoid smoking & alcohol – lowers toxin exposure.
- Maintain healthy weight (low BMI, reduced visceral fat)
When to Call Your Healthcare Provider
Call a doctor if you notice:
- Severe or sudden muscle weakness
- Persistent joint pain or swelling
- Signs of infection (fever, rash, chest pain)
- Unexplained fatigue or cognitive decline
- Chronic digestive imbalance (diarrhea, constipation, reflux)
- Early detection prevents long-term damage.
Final Thoughts
Recognizing the signs of inflammation in the body can save you from years of silent damage. While acute inflammation helps you heal, chronic inflammation is a warning sign that your immune system is stuck in overdrive.
By focusing on an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, eating healing nutrients,exercising, reducing stress, and avoiding pro-inflammatory foods you can lower your risk of chronic disease, boost your energy, and protect your long term health.When in doubt, always consult a healthcare provider for professional medical advice.
If you enjoyed this article and would like to read more like it, please check out the rest of our blog today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the first signs of inflammation in the body?
Redness, swelling, pain, heat, fatigue, and muscle weakness.
Can inflammation cause brain fog and memory loss?
Yes, neuroinflammation affects brain function, leading to cognitive decline.
Is inflammation always bad?
No. Acute inflammation is protective, but chronic inflammation can harm tissues.
What foods reduce inflammation quickly?
Fatty fish, leafy greens, olive oil, turmeric, berries, nuts.
Can stress cause inflammation?
Yes. Chronic stress triggers hormonal imbalance and inflammatory pathways.
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience severe weakness, persistent swelling, chest pain, or unexplained fatigue.